Language/Java
[Java] 실습 (Exception)
arajo
2022. 8. 24. 21:22
728x90
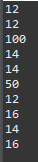
0은 나눌 수 없다. 에러가 발생할 수 있음
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 100;
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// number를 임의의 정수(0~9)를 추출하여 나눈 결과를 보여준다.
result = number / (int)(Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
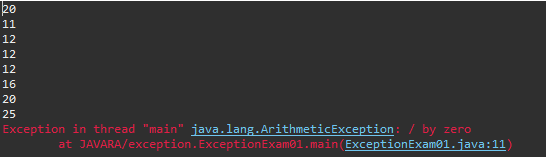
try...catch 사용
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 100;
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
result = number / (int)(Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println("숫자를 0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
}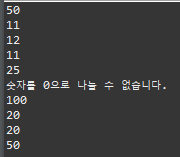
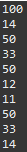
순서
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
try {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(4);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(5);
}
System.out.println(6);
}
}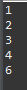
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
try {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(0/0);
System.out.println(4);
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) {
System.out.println(5);
}
System.out.println(6);
}
}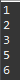
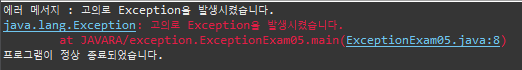
고의로 Exception 발생
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Exception e = new Exception("고의로 Exception을 발생시켰습니다.");
throw e; // 예외를 발생시킨다.
// 위의 두 줄을 한줄로 줄여 쓸 수 있다.
// throw new Exception("고의로 Exception을 발생시켰습니다.");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("에러 메서지 : " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("프로그램이 정상 종료되었습니다.");
} // e.getMessage(), e.printStackTrace() 자주씀
}
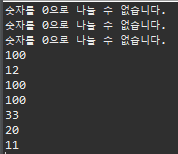
아래로 갈 수록 범위가 넓어야 한다.
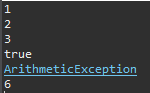
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
try {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(0/0);
System.out.println(4); // 이 구문은 실행이 되지 않는다.
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) { // 여러개의 익셉션은 아래로 갈 수록 범위가 넓어야 한다.
if(ae instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("true");
System.out.println("ArithmeticException");
} catch (Exception e) { // ArithmeticException을 제외한 모든 에러가 처리된다.
System.out.println("Exception");
}
System.out.println(6);
}
}
printStackTrace(), getMessage()
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// printStackTrace() - 예외발생 당시의 호출스택(Call Stack)에 있었던 메서드의 정보와
// 예외 메세지를 화면에 출력한다.
// getMessage() - 발생한 예외클래스의 인스턴스에 저장된 메세지를 얻을 수 있다.
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
try {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(0/0); // 예외 발생
System.out.println(4); // 실행되지 않는다.
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) {
// 참조변수 ae를 통해서 생성된 ArithmeticException인스턴스에 접근할 수 있다.
ae.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("예외 메세지 : " + ae.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(6);
}
}
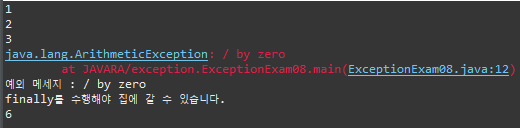
finally
package exception;
public class ExceptionExam08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
try {
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(0/0);
System.out.println(4);
} catch (ArithmeticException ae) {
ae.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("예외 메세지 : " + ae.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally를 수행해야 집에 갈 수 있습니다.");
}
System.out.println(6);
}
}
finally는 무조건 실행, 마지막에 쓴다.